
라즈베리파이와 하드로 NAS를 구축한지도 4년 즈음 됐다. 처음에는 아무것도 몰라서 기본 환경에다가 이것저것 설치했었는데, 이것들이 시간이 지나니 포트도 뒤죽박죽에 충돌도 났다. 이런 취미를 공유하는 친구가 한 명 있는데, 그 친구가 Docker 를 왜 안쓰냐고 그래서 시작했다. 모든 자체 호스팅(Selfhosted) 웹서비스를 도커로 마이그레이션하기로 마음을 먹었다.
1. 왜 너만 안돼
Nextcloud. 정말 편리하게 쓰는 클라우드 앱이다. 원래는 OwnCloud였는데 얘네가 수익화를 시작해서 떨어져나왔다고 한다. 오픈소스고, 데스크탑/모바일 앱도 있다. 서버 리소스를 혼자만 쓰니 빠르고, 에러도 잘 안난다. 개인적으론 구글 드라이브보다 더 좋다. 다만 단점이라면, 세팅하기가 어렵다는거.
도커 컴포즈로 설치하려니 너무 복잡했다. 여타 블로그 글들 복붙하니 안되고, 겨우 찾아서 해보니까 너무 느리다. 어찌저찌 하고 나니 동작은 잘 되는데, SMB가 지원되지 않아서 외부 드라이브를 연결할 수 없었다. 알고보니 이친구 스펙별로 지원되는 버전이 너무 많다. 그래서 블로그에 정리해둔다.
docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
volumes:
data:
db:
services:
db: # 1. DB는 왜 써?
image: mariadb:10.6
command: --transaction-isolation=READ-COMMITTED --log-bin=binlog --binlog-format=ROW
restart: always
volumes:
- ./db:/var/lib/mysql
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=
- MYSQL_PASSWORD=
- MYSQL_DATABASE=nextcloud
- MYSQL_USER=nextcloud
- MARIADB_AUTO_UPGRADE=1
- MARIADB_DISABLE_UPGRADE_BACKUP=1
app: # 2. 무슨 버전을 써야돼?
image: nextcloud:fpm-alpine
build:
context: .
restart: always
volumes:
- ./data:/var/www/html:z
- /path/to/storage:/mnt/storage # 3. 저장공간 마운트?
environment:
- MYSQL_PASSWORD=
- MYSQL_DATABASE=nextcloud
- MYSQL_USER=nextcloud
- MYSQL_HOST=db
links:
- db
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-file: "5"
max-size: "100m"
web: # 4. Nginx 왜 써?
image: nginx
restart: always
ports:
- 8004:80
links:
- app
volumes:
- ./nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:ro
volumes_from:
- app
Dockerfile
FROM nextcloud:fpm-alpine
RUN apk add --no-cache procps samba-client현재 셋업이다.
자세한 내용은 https://hub.docker.com/_/nextcloud
nextcloud - Official Image | Docker Hub
Note: the description for this image is longer than the Hub length limit of 25000, so has been trimmed. The full description can be found at https://github.com/docker-library/docs/tree/master/nextcloud/README.md. See also docker/hub-feedback#238 and docker
hub.docker.com
에서 찾아볼 수 있다.
(1) DB는 왜 써?
도커로 이미지를 풀링 하다보면, 이런 의문이 든다. 그냥 간단하게, Nextcloud 이미지 하나만 받아서 쓸 순 없는건가? 알고보면, 얘네가 필요한 이유가 따로 있다.
기본 탑재되어있는 Sqlite를 쓰면, 경고 메시지가 뜬다. 도커 이미지에 기본적으로 sqlite가 깔려 있는데, 이는 기능이 너무 없어서 너무 느리거나 에러가 발생할 수 있다고 한다. 그래서 실제로 실행해보면, Sqlite를 쓰면 초기설정에 시간이 오래걸리고, MariaDB(MySQL)를 쓰면 거의 바로 되는걸 알 수 있다.
(2) 무슨 버전을 써야돼?

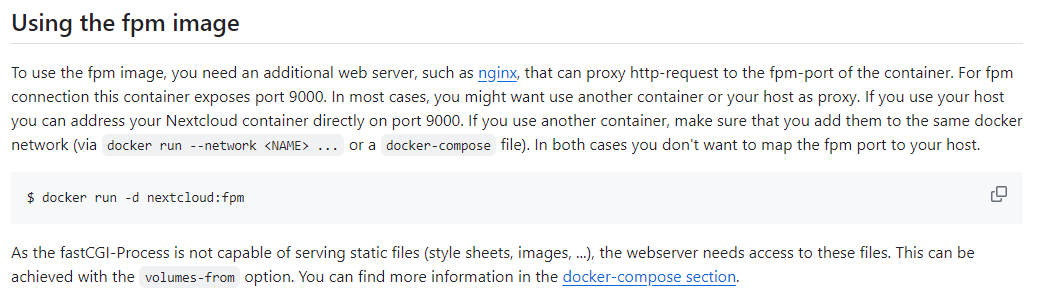
fpm 이미지를 쓰면 apache 말고 nginx같이 다른 리버스 프록시를 사용할 수 있다. 이 방법이 웹사이트 로딩시간을 획기적으로 줄여준다. 또한, 만약 smb나 imap같은 서비스를 사용하고 싶다면, Dockerfile을 수정하여 관련 dependency를 추가해줘야 한다. (물론 full을 쓰면 다 되는거긴 한데, 용량을 너무 많이 차지한다.)
에서 찾아볼 수 있다.
(3) 저장공간 마운트

로컬 폴더를 docker-compose에 명시해주면 외부 저장소의 "로컬" 옵션을 통해 마운트할 수 있다.
(4) Nginx 사용하기
nginx는 그냥 nginx 오피셜 이미지를 가져와서 쓰는데, 저장공간을 app(nextcloud)과 공유한다. 따라서 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 를 ":ro"(read only) 태그와 함께 매핑하면, 이 설정파일을 nginx가 읽어서 앱을 웹상으로 띄운다.
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
# Prevent nginx HTTP Server Detection
server_tokens off;
keepalive_timeout 65;
# Set the `immutable` cache control options only for assets with a cache busting `v` argument
map $arg_v $asset_immutable {
"" "";
default "immutable";
}
#gzip on;
upstream php-handler {
server app:9000;
}
server {
listen 80;
# HSTS settings
# WARNING: Only add the preload option once you read about
# the consequences in https://hstspreload.org/. This option
# will add the domain to a hardcoded list that is shipped
# in all major browsers and getting removed from this list
# could take several months.
#add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=15768000; includeSubDomains; preload;" always;
# set max upload size and increase upload timeout:
client_max_body_size 512M;
client_body_timeout 300s;
fastcgi_buffers 64 4K;
# The settings allows you to optimize the HTTP2 bandwidth.
# See https://blog.cloudflare.com/delivering-http-2-upload-speed-improvements/
# for tuning hints
client_body_buffer_size 512k;
# Enable gzip but do not remove ETag headers
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_comp_level 4;
gzip_min_length 256;
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private no_last_modified no_etag auth;
gzip_types application/atom+xml text/javascript application/javascript application/json application/ld+json application/manifest+json application/rss+xml application/vnd.geo+json application/vnd.ms-fontobject application/wasm application/x-font-ttf application/x-web-app-manifest+json application/xhtml+xml application/xml font/opentype image/bmp image/svg+xml image/x-icon text/cache-manifest text/css text/plain text/vcard text/vnd.rim.location.xloc text/vtt text/x-component text/x-cross-domain-policy;
# Pagespeed is not supported by Nextcloud, so if your server is built
# with the `ngx_pagespeed` module, uncomment this line to disable it.
#pagespeed off;
# HTTP response headers borrowed from Nextcloud `.htaccess`
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies "none" always;
add_header X-Robots-Tag "noindex, nofollow" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
# Remove X-Powered-By, which is an information leak
fastcgi_hide_header X-Powered-By;
# Path to the root of your installation
root /var/www/html;
# Specify how to handle directories -- specifying `/index.php$request_uri`
# here as the fallback means that Nginx always exhibits the desired behaviour
# when a client requests a path that corresponds to a directory that exists
# on the server. In particular, if that directory contains an index.php file,
# that file is correctly served; if it doesn't, then the request is passed to
# the front-end controller. This consistent behaviour means that we don't need
# to specify custom rules for certain paths (e.g. images and other assets,
# `/updater`, `/ocm-provider`, `/ocs-provider`), and thus
# `try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$request_uri`
# always provides the desired behaviour.
index index.php index.html /index.php$request_uri;
# Rule borrowed from `.htaccess` to handle Microsoft DAV clients
location = / {
if ( $http_user_agent ~ ^DavClnt ) {
return 302 /remote.php/webdav/$is_args$args;
}
}
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# Make a regex exception for `/.well-known` so that clients can still
# access it despite the existence of the regex rule
# `location ~ /(\.|autotest|...)` which would otherwise handle requests
# for `/.well-known`.
location ^~ /.well-known {
# The rules in this block are an adaptation of the rules
# in `.htaccess` that concern `/.well-known`.
location = /.well-known/carddav { return 301 /remote.php/dav/; }
location = /.well-known/caldav { return 301 /remote.php/dav/; }
location /.well-known/acme-challenge { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; }
location /.well-known/pki-validation { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; }
# Let Nextcloud's API for `/.well-known` URIs handle all other
# requests by passing them to the front-end controller.
return 301 /index.php$request_uri;
}
# Rules borrowed from `.htaccess` to hide certain paths from clients
location ~ ^/(?:build|tests|config|lib|3rdparty|templates|data)(?:$|/) { return 404; }
location ~ ^/(?:\.|autotest|occ|issue|indie|db_|console) { return 404; }
# Ensure this block, which passes PHP files to the PHP process, is above the blocks
# which handle static assets (as seen below). If this block is not declared first,
# then Nginx will encounter an infinite rewriting loop when it prepends `/index.php`
# to the URI, resulting in a HTTP 500 error response.
location ~ \.php(?:$|/) {
# Required for legacy support
rewrite ^/(?!index|remote|public|cron|core\/ajax\/update|status|ocs\/v[12]|updater\/.+|ocs-provider\/.+|.+\/richdocumentscode\/proxy) /index.php$request_uri;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+?\.php)(/.*)$;
set $path_info $fastcgi_path_info;
try_files $fastcgi_script_name =404;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $path_info;
#fastcgi_param HTTPS on;
fastcgi_param modHeadersAvailable true; # Avoid sending the security headers twice
fastcgi_param front_controller_active true; # Enable pretty urls
fastcgi_pass php-handler;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_request_buffering off;
fastcgi_max_temp_file_size 0;
}
# Javascript mimetype fixes for nginx
# Note: The block below should be removed, and the js|mjs section should be
# added to the block below this one. This is a temporary fix until Nginx
# upstream fixes the js mime-type
location ~* \.(?:js|mjs)$ {
types {
text/javascript js mjs;
}
default_type "text/javascript";
try_files $uri /index.php$request_uri;
add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=15778463, $asset_immutable";
access_log off;
}
# Serve static files
location ~ \.(?:css|svg|gif|png|jpg|ico|wasm|tflite|map|ogg|flac)$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$request_uri;
add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=15778463, $asset_immutable";
access_log off; # Optional: Don't log access to assets
location ~ \.wasm$ {
default_type application/wasm;
}
}
location ~ \.woff2?$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$request_uri;
expires 7d; # Cache-Control policy borrowed from `.htaccess`
access_log off; # Optional: Don't log access to assets
}
# Rule borrowed from `.htaccess`
location /remote {
return 301 /remote.php$request_uri;
}
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$request_uri;
}
}
}
코드에 쓸데없는 구문이 많은 느낌인데, 수정할 시간이 없어 아직 이걸 쓴다. 중요한 부분은 listen 80; 부분이고, nginx가 읽을 부분은 root /var/www/html 부분이다. 도커와 저장공간을 공유하기 때문에 복붙하면 맞을 것이다.
ssl 암호화는 여기서는 진행하지 않고, Nginx Proxy Manager를 통해 진행했다. 이는 다른 글에서 별도로 다루겠다.
'프로젝트 > 설명' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 라즈베리파이 - 리눅스 시스템 구조 (0) | 2021.11.10 |
|---|---|
| 카페24 쇼핑몰 3. 스마트 디자인 이해하기 (1) | 2021.10.22 |
| 카페24 쇼핑몰 2. 개발환경 세팅하기(FTP) (0) | 2021.10.22 |
| 카페24 쇼핑몰 1. 시작하기 (0) | 2021.10.22 |
| 디스코드봇 6. 코드의 원리 파악하기 (3) 객체 지향과 공식문서 활용법 (0) | 2020.12.20 |
